The objective of the process is to provide users with the necessary rights to use a service or group of services. This process applies security policies defined in the information security management process.
The management of access rights or identity management provides organizations with only authorized users having access to their data. This allows, in particular, the reduction of the risk of intrusions and attacks and protects the integrity of their data. Good identity management also simplifies the experience of your users.
Access management is the process of providing authorizations to clients/users that have the right to a service, unlike others who do not have access. It gives access depending on a user's services, groups or functions. Identity management, privacy, integrity, and availability are meanwhile also known as management of access rights and touch the withdrawal of access for people who change roles or positions and regular audit of permissions given to different security groups.
Defining Access Management and Identity Process
Here are three key processes for Identity Management :
1. Modeling the Access Process
- It consists mainly of four steps: create, change, and report a problem or use of the access model.
- Security management is done by standards and company policies also, including government regulations and industry.
- These policies allow the construction of roles and rules to be used for the creation and management of identity.
- Establish a structure based on rules or according to the role (creating roles, privileges, rules and policy).
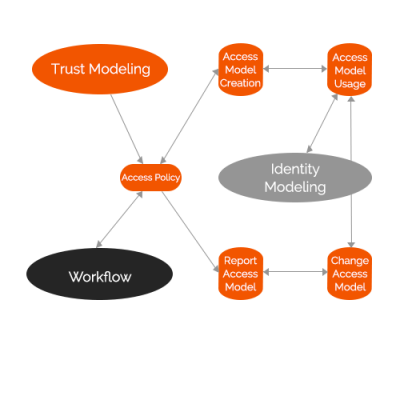
2. Optimizing of the Workflow
- This is how to interact with the access process model once it is available to the organization. This is also how to generate “output” (roles, rules and associated information).
- Mainly used for approval/authorization.
- Once the workflow is created it will be possible to use it, change it or relate it to the workings of generating modifications.
3. Modeling the Identity Process
- This is where individual identities are created using the access and workflow processes.
- An identity in this process is the minimum set of associated attributes required for the maximum number of applications and services to achieve authentication and authorization.
- It is not a question of a complete collection of related identity data.
- The identity process modeling mainly creates, uses, modifies, revokes, “monitor”, and remove access.
- When a new resource needs access for the first time, it must be created based on the models and workflow in place.
Access Management according to ITIL
1. Documentation
- Creation of a catalog of roles and access profiles
- Ensure that the roles and access profiles are still adequate for the service offered to the customer.
- Prevent the accumulation of unnecessary access rights.
2. Establishment of an application access process
- Allows for requests to add or revoke modifications and ensures that the user has the rights to obtain access.
Impact on the assignment of an ITSM tool
Setting up your catalogs:
- The first step in establishing security in your ITSM.
- Only permits access to applications that a user has the right and ensures that it does not exceed the scope of his duties.
- Allows you to filter by application type (change request, service request, incident, problem), for equipment or applications.
- Considers the Human Resources Department where all employees of a company do not have the right to request the arrival or departure of employees. These requests are reserved for executives of a company and are not part of your basic catalog. You will need to create a second more extensive catalog for this group.
- The same principle applies for problem-type requests or requests with another subject that you want to reserve only to resources without giving access to customers.
- In setting up your workflow you might also have levels of approval to a request, which also limits the rights of clients.
Security Management Application:
- You will be able to manage the security of your resources within the application by providing access to certain features.
- For example, a resource group might have read-only access while a super user group would have the rights of reading and writing.
- All resources might be able to change an address or password, but not create new users.
If you apply the mentioned processes and management activities, you will be able to build a safe and efficient access management for your organization.